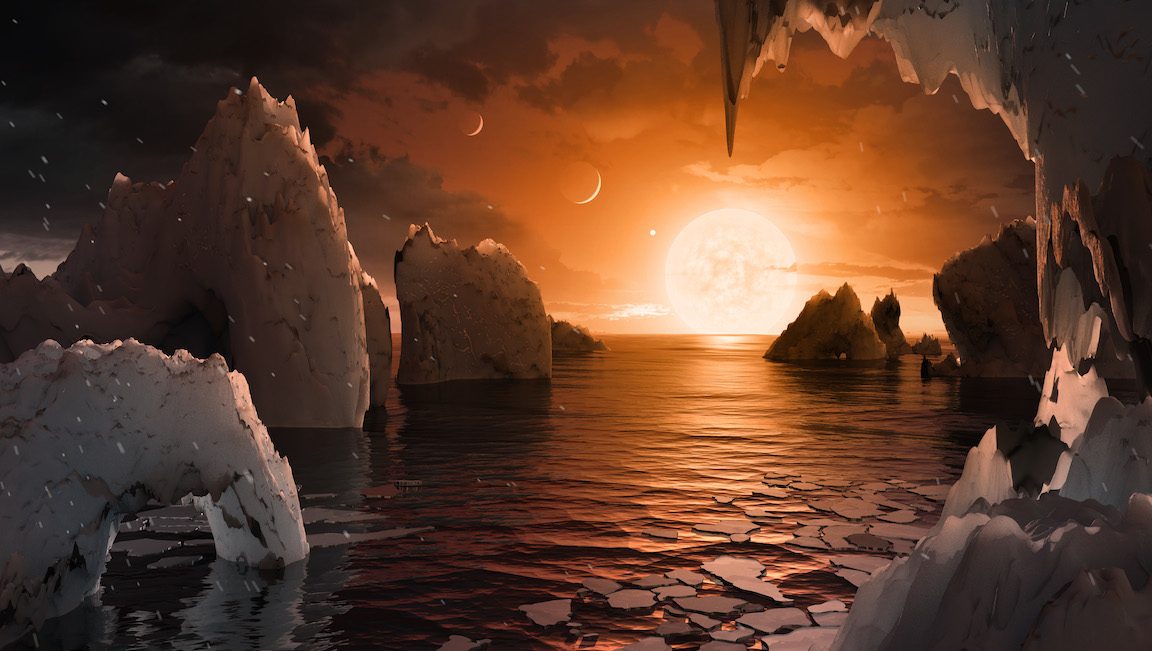
Pictured above, there’s a landscape from the Trappist-1 system, which has seven Earth-like worlds orbiting a dwarf star.
This is not a photo, however, as it is not possible to take those for the time being. All NASA has are blips on a data readout.
Yet when concept artists get involved, scientists can guide them to create something beautiful, evocative, and still surprisingly plausible. The result is that the general public can get more excited about distant discoveries. (After all, NASA doesn’t come cheap.)
They even help scientists discuss their own work and explain the value of understanding worlds beyond ours.
To learn more about the process of creating NASA’s remarkable visualizations in Wired, click here.
This article appeared in an InsideHook newsletter. Sign up for free to get more on travel, wellness, style, drinking, and culture.