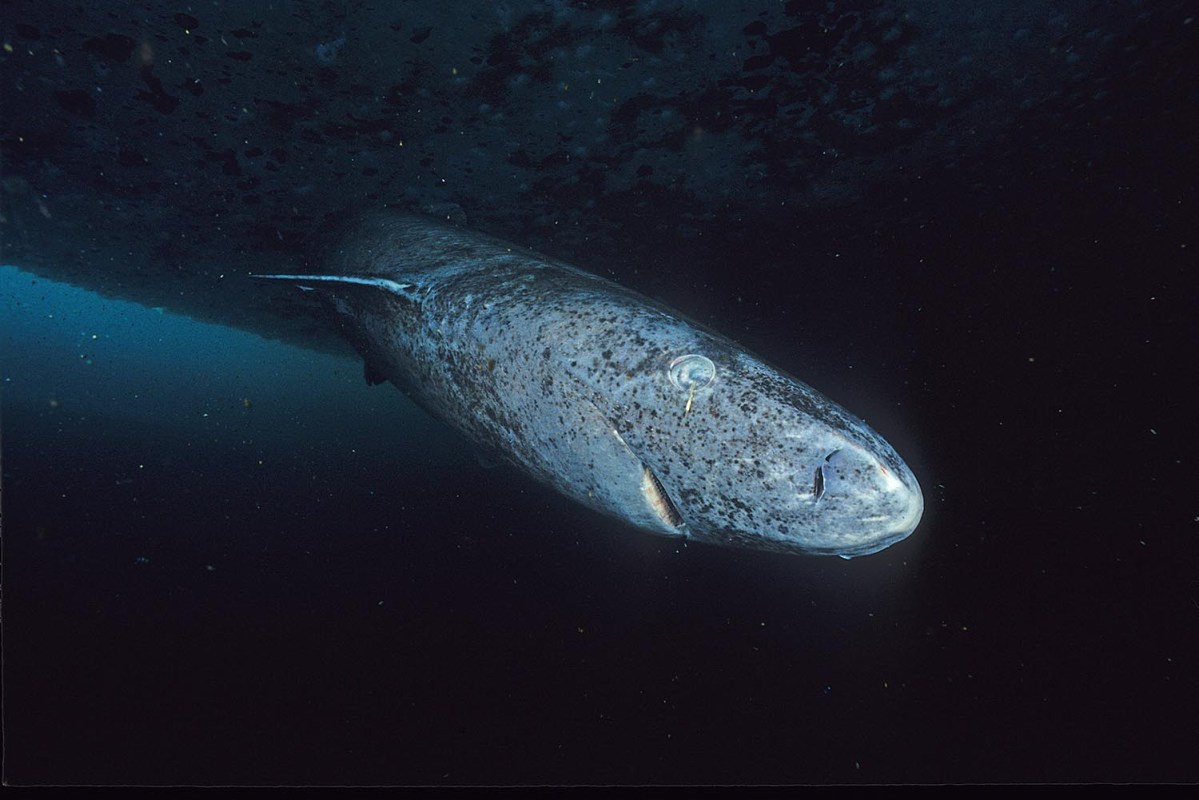
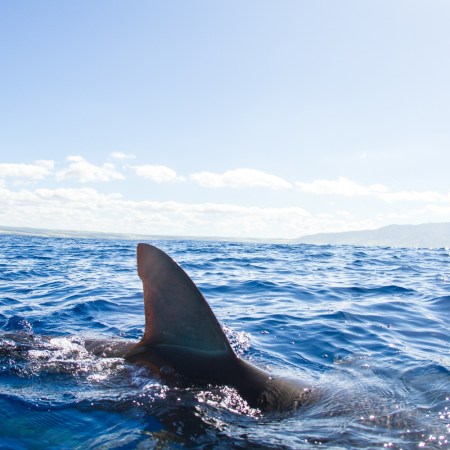
Are there vertebrates occupying the planet today whose lifespans extend back to before the founding of the United States? Based on recent research, it seems very likely — and they exist in the form of sharks whose fermented meat are used in a very distinctive Icelandic dish. Scientists have found evidence that Greenland sharks live for hundreds of years — and that there are some whose lifespans extend to 400 or even 500 years.
For some scientists, the lengthy lifespans of certain creatures can also have an impact on research into making humans live longer. That’s true for the immortal jellyfish, and it also applies to the Greenland shark. A recent article by Jonathan Moens at Atlas Obscura explores what scientists have learned from their studies of the long-lived sharks — and what it might mean for humanity.
Greenland sharks’ longevity could be chalked up to genetic or lifestyle factors, or some combination of the two. The University of Manchester’s Holly Shiels suggested that, as Moens writes, “Greenland sharks may have a uniquely sophisticated system to repair damaged DNA.” Other scientists point to the sharks’ habitat — cold Arctic waters — and their ability to live for a long period of time on a relatively small amount of food as signs of a very efficient metabolism.
This isn’t to say that everything about the long lives of these sharks sounds enviable — including the idea that they might not become sexually mature until the age of 150. But for the growing body of research on aging, the Greenland shark offers a host of invaluable information.
Thanks for reading InsideHook. Sign up for our daily newsletter and be in the know.